Each industry and each field of activity has its own terminology that is associated with it. For the IT sphere, they are UX and UI design. They are both closely tied and they are both critical components that are needed to ensure user satisfaction. However, they are not exactly the same.
Before we dive deeper into the specifics and the differences between them, we need to clarify what UI and UX mean separately.
What is UI design? 🐱💻
UI stands for user interface. UI design is the creation of all the visual components of the interface. In other words, this is most of the elements that can be seen and heard by users.
The visual interface ensures efficient interaction between the human and the computer. Using tools like graphic editing software and other programs for visual content, UI designers prepare various layout mockups and style tiles. UI designers make graphic and text information pleasant and attractive, thereby creating an emotional connection between the user and the interface.
The main aim of UI design is to offer the simplest solutions for interaction with software with the help of visual elements. The right UI design makes the usage of an app or website intuitively clear.
Today, the work of UI designers is not limited to the creation of computer interfaces only. They also have to deal with smartphones, various mobile devices, and other gadgets.
What is UX design?🐱👤
UX means user experience. This experience is a result of human-computer interaction.
UX design is aimed at creating positive user interaction with the interface. The principles of UX design are based on the results of user behavior and experience analysis.
UX designers develop scenarios of how and what goals a user can achieve when interacting with a digital product.
It’s more than just usability. User experience depends on various components: site architecture, graphic design, clear text, and responsiveness of the interface to specific user actions.
User experience starts the moment a user looks for the product, but it doesn’t end when a user switches off the device.
According to Peter Morville, one of the most prominent experts in areas such as information architecture and user experience, UX design is effective when it represents a combination of characteristics such as:
- usefulness
- usability
- value
- desirability
- credibility
- accessibility
- findability.
In their work, UX designers cooperate with UI, marketing and product teams in order to gather information about user expectations and needs. Analyzing the data, UX designers create site maps, prototypes, and wireframes.
When the product is launched, their work still continues. Based on the real experience of users, these specialists can offer valuable improvements to bring the level of user satisfaction higher.
Examples of UI and UX design
Now we’d like to offer some examples of UI/UX design to sort things out and clarify all controversial and incomprehensive moments.
Let’s imagine that you are looking for a hotel to book for your vacation. You open a website and see that everything looks quite pleasant; all the buttons are placed where they should be, there is a convenient search form, and in general, the interaction is organized in a very comfortable way.
This means that the UI designers have done a good job.
But suddenly you realize that all the hotels are overpriced and there are no options for your budget. Moreover, you find that you have to wait more than a minute for the answer to your request (let’s suppose that everything is okay with your internet connection).
Obviously you’ll be disappointed with such an experience. What are we speaking about now? User experience, which is not as positive as it should be in this case. UX designers haven’t taken into account the expectations of users, which caused a negative reaction.
UX designers should place users at the center of their attention and should focus on their needs. For example, if you want to create a payment app, UX designers have to consider the convenience of interaction with it, the time needed for payments, and the interface of this application.
Do not forget the fact that excellent user experience is impossible without good UI design. Only their combination can guarantee the best user experience ever.
UX and UI: differences
As you may already understand, there is a big difference between UX and UI, but they still go together. To put this difference as simply as possible, let us turn to one very vivid comparison.
What if we said that UI is a part of UX like a road is part of a journey?
Can we compare a road and a journey? Probably. However, wouldn’t it be better not to compare them but to show how the choice of the road can affect your experience of the entire journey or how the destination you have chosen for your journey affects your possibilities to choose a road?
UI helps you move along your road that depends on the type of journey you have opted for. If your route is well-planned, it will be easy for you to keep track of your road. The same goes for any user interface. While it is logically structured and intuitively clear, it won’t be a problem for you to move forward. When UI is poor, you will easily get lost.
Your journey itself is affected by many factors, including weather, people around you, beautiful scenery, interesting locations, and many other things, like the quality of the road. At the end of any journey you always make a conclusion on whether you’ve managed to reach your goal. User experience is also about reaching your goals.
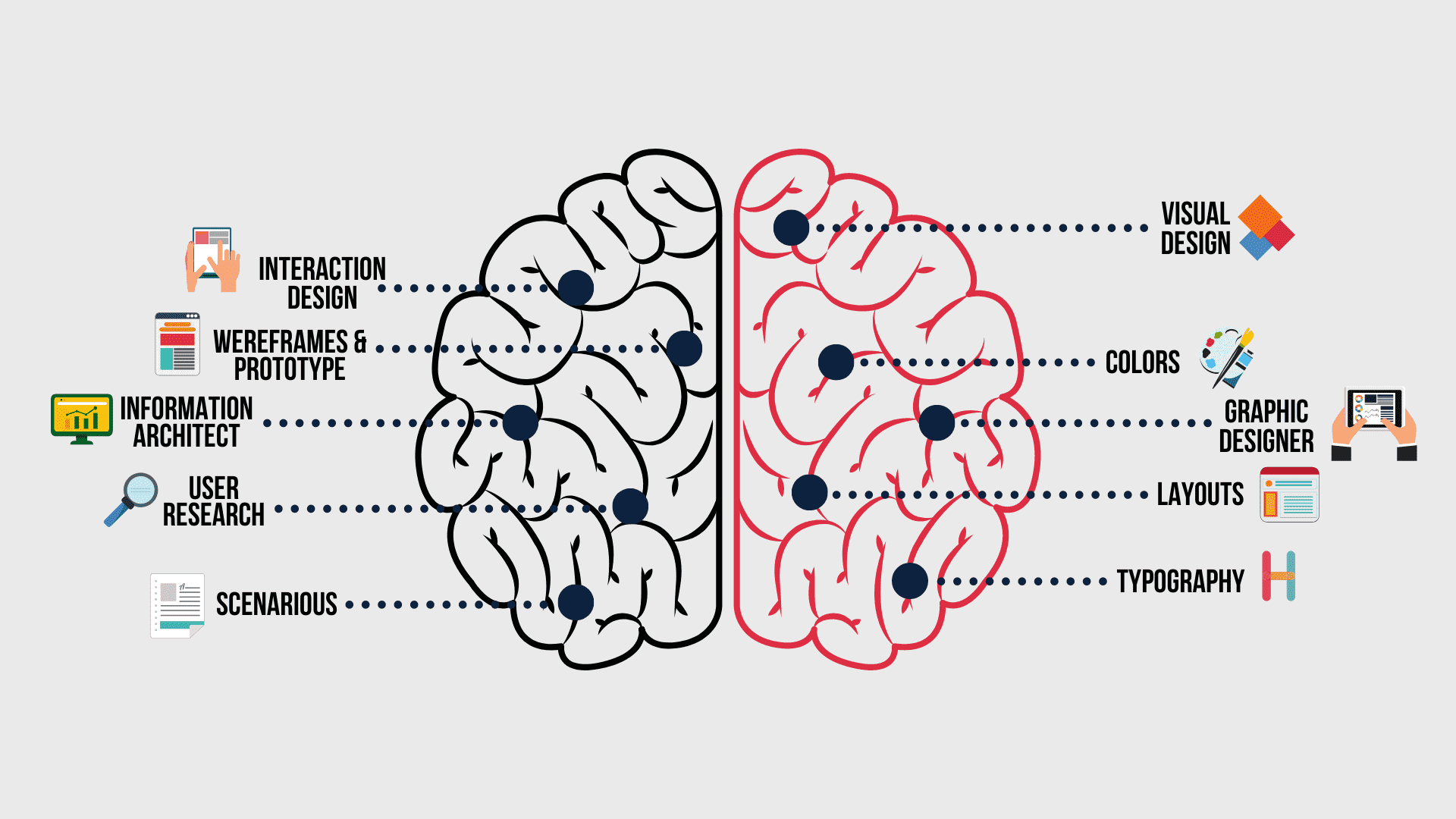
What are the core differences between UI and UX?
User-experience is a more complicated notion. It is influenced by many factors, including UI, and it stays with you much longer than the time you spend interacting with the website.
- Visual representation vs Emotions
UI is a final result of designers’ work; it’s a complex of various elements that a user will see. It includes buttons, icons, pages, and forms which help us interact with any software. At the same time, UX is a complex of users’ impressions. Our inner feelings and emotions do not have any physical representation in the real world and they are unique for every single person on earth.
From this perspective, UI differs from UX like a scenery you are watching or a book you are reading differs from the feelings you have at this time.
- Short-term interaction vs Long-term effect
You interact with UI only while you are working with a web site or app. In other words, UI provides you tools to interact with a site. As soon as you close your browser, you may forget about where some buttons are located or what icons are placed in the left corner.
User-experience is a more complicated notion. It is influenced by many factors, including UI, and it stays with you much longer than the time you spend interacting with the website.
Even when you switch off your laptop or mobile device, your UX is still being formed (for example, when you think about the solution that the product has offered you or when you describe this app to your friends).
In this case, we can come back to our first comparison of UI and UX with a road and journey. While you are travelling, you think about both the road and the journey itself. However, later you will analyze your journey only in the whole (unless someone asks you about the road itself).
Summary👍
As you see, UX and UI design can’t be viewed as the same things (in general, they are absolutely different). In fact, they are closely connected and can’t exist without each other. UI design logically follows the principles of UX. So sometimes the line between them is blurred. At the same time, UX is a much wider field and presupposes the involvement of some knowledge from other areas, including marketing and even psychology.


